The Latitudes indicate, how far north or south a particular place is from the Equator. But to accurately spot a place, the north-south lines are needed to intersect the parallels. Cutting across the lines of Latitude, are lines running from north to south, known as the ‘lines of Longitude’ or ‘Meridians’. The word ‘Meridian’ is originated from the Latin word ’meredies’ meaning midday. Since all the places on the same line of longitude have their midday at the same time, each line of Longitude is called ‘meridian’. These lines are drawn by joining the two Poles through 360 divisions marked at an interval of 1º on the Equator. These meridians together with the parallels of Latitudes complete the network of lines called the ‘Earth Grid’.
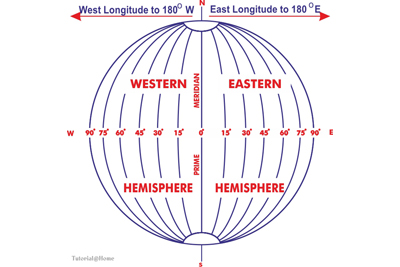
Unlike the Equator, any line of Longitude could have been used for measuring east-west distance, since each Meridian is a half circle and has the same size. Therefore, by an international agreement in 1884, the line of longitude that passes over the Royal Astronomical Observatory at Greenwich was chosen as the 0º longitude. It is also known as the ‘Prime Meridian’ or the ‘Zero Meridian’. All the other lines of longitudes are drawn east or west of the Prime Meridian. Each of them extends from the North Pole to the South Pole and forms a semicircle. Drawn at interval of 1º, there are 360 lines of Longitude, including the Prime Meridian. These 360 lines are divided into two groups of 180 each – 180 lines to the east and 180 lines to the west of the Prime Meridian. The lines lying to the east of the Prime Meridian are known as ‘East Longitudes, while the lines to the west of the Prime Median are called ‘West Longitudes’. However, the 180th line is one line only, it is the same for both the east and the west longitudes. So it is not called East or West, but simply the 180º Longitude.

The Longitude of a place is, therefore, its angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. It is measured in degrees from the centre of the Earth. On the other hand, the Meridians of Longitude are the lines joining places having the same Longitude.
The lines of Longitudes come closer and closer together with increasing distance from the Equator and finally converge at the Poles. So the distance between two adjacent Meridians varies. At the Equator 1º equals 111 km, at 60º north or south it is 55’4 km and at the Poles it is nil.

It is totally impossible to accurately locate a particular place on the vast expanse of the Earth’s surface, without the help of Latitudes and Longitudes. For example, let us take the case of Kolkata, which lies on 88º24’E meridian of Longitude. But, 88º24’E meridian of Longitude extends from the North to the South Pole and countless places lie on that Meridian. Hence, it is necessary to know its Latitude, to ascertain how far north or south Kolkata lies from the Equator. As Kolkata lies on the 22º34’N parallel of Latitude, its exact location would be at the point of intersection of 88º24’E Longitude and 22º34’N Latitude.