
Newton’s law of motion was put forwarded by Sir Isaac Newton (an English scientist) in the year of 1686. He put forwarded three laws about the motion, which are known as Newton’s laws of motion. Here we discuss about the third law of them.
Defination:
Every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
If a body applies force on another body then that force is known as action. The second body is also applies equals and opposite force to the first body, that force is known as reaction. That is, if a force applies on a body in a particular direction then that body also apply same force toward the opposite direction.
An apple drops on field or surface of earth from the tree. As we know action have an equal and opposite reaction, then why earth is not forward to the apple?
Here, action and reaction are equal and opposite; therefore applied force on earth by the apple is same as the force applied by the earth on apple. But let the force applied by apple is F1 and the force applied by earth is F2.
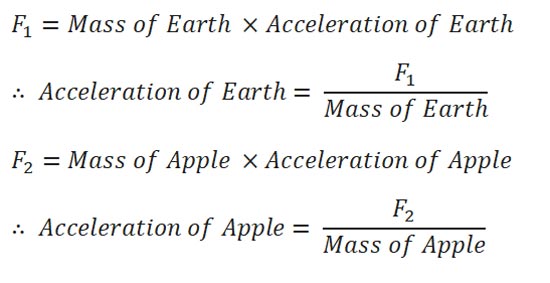
As we know F1 = F2, therefore, Acceleration apple is huge in compare to acceleration of earth. That is why apple is drop in the earth.
Examples of Newton’s third law.
The boatman ties his boat before allowing the passengers to disembark:
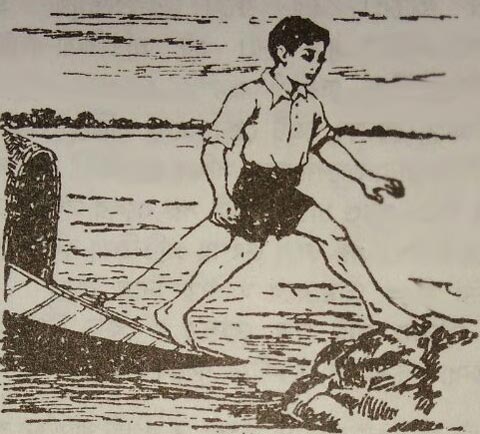

This due to the fact that when the passengers start disembarking (getting out of the boat), they push the boat backward with their feet (action). The boat also apply an equal and opposite force on the passengers in the forward direction (reaction). Since the boat is in water, it moves backward due to the action force exerted by the passengers. So the boatman ties his boat to prevent the boat from sliding back in the water.
Rowing of a boat:

During the rowing of a boat, the boatman pushes the water backwards with the oars (action). According to newton’s third law of motion, the water apply an equal and opposite push on the boat which moves the boat forward (reaction).