
font-family property set the font of the text in the web page. We should mention more than one font in a row. Because if browser cannot find the first font then it try to find the second one and so on. this process known as "fallback". In this case we start with the font which we are want to use and end with a generic family.
Note: The multi word font name like Monotype Corsiva should be written as "Monotype Corsiva". i.e. under a quotation marks.
CSS CODE
DIV
{
font-family:'monotype corsiva',Verdana, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
HTML CODE
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Font Family Demo</title>
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
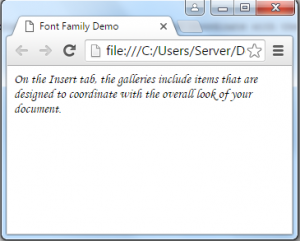
<div>On the Insert tab, the galleries include items that are designed to coordinate with the overall look of your document. </div>
</body>
</html>
Note: Some time our given font are not found on every machine then browser choose the generic font. That may cause the look of the web pages are change. To slove this problem now developers used google font. We just connect a css file of google.com by the following syntax. Through URL parameters, we specificify which fonts we want, and what variations of those fonts.
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Tangerine:bold,bolditalic|Inconsolata:italic|Droid+Sans">
That may create another problem, If google.com server is down for some reson then our site will aslo stop. To avoid this situation we can downloading the stylesheet and copy-and-pasting the @font-face stuff into our main stylesheet. But we also lost the all update from google.
After linking this file we can able to write the following code into out CSS file
body
{
font-family: 'Tangerine', 'Inconsolata', 'Droid Sans', serif;
font-size: 48px;
}
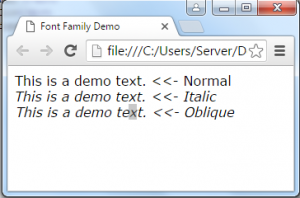
The font-style property is used to set the font style of the text.
There are three types of style is:
CSS CODE
DIV
{
font-family:Verdana, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.normal
{
font-style: normal;
}.italic
{
font-style: italic;
}.oblique
{
font-style: oblique;
}
HTML CODE
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Font Family Demo</title>
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="normal"> This is a demo text. <<- Normal </div>
<div class="italic"> This is a demo text. <<- Italic</div>
<div class="oblique"> This is a demo text. <<- Oblique</div>
</body>
</html>
font size of the text is set by the font-size properties of CSS.
Note: we can set the size of the any HTML tag like Heading(H1, H2, ...), Paragraph etc. But we ethically not allowed to adjust the font as pragraph look like heading and heading look like paragraph. We must follow the basic sequence of the font that is, <H1>....<h2>, <p>.
Note: The default font size for paragraph, is 16px or 1em.
Absolute size : It is used for the known physical output.
Relative size : It is used when user want to change the font size according to the size of the output devices.
CSS CODE
DIV
{
font-family:Verdana, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.SizeInPx
{
font-size: 40px;
}.SizeInEm
{
font-size: 1.5em; /* 24px/16=1.5em */
}
.SizeInPercentage
{
font-size: 100%;
}
HTML CODE
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Font Family Demo</title>
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="SizeInPx"> This is a demo text. <<- Size In Px </div>
<div class="SizeInEm"> This is a demo text. <<- Size In Em</div>
<div class="SizeInPercentage"> This is a demo text. <<- Size In Percentage</div>
</body>
</html>

The boldness of the text is set by the font-weight property of CSS
CSS Code
DIV
{
font-family:Verdana, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.normal
{
font-weight: normal;
}.Heavy
{
font-weight: bold;
}
HTML Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Font Weight Demo</title>
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="normal"> This is a demo text. <<- normal </div>
<div class="Heavy"> This is a demo text. <<- Heavy</div>
</body>
</html>

Whether the text in a web page displayed in a small-caps format or normal format is determined by font-variant property of CSS.
CSS CODE
DIV
{
font-family:Verdana, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
.normal
{
font-variant: normal;
}.small
{
font-variant: small-caps;
}
HTML CODE
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Font Variant Demo</title>
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="normal"> This is a demo text. <<- normal </div>
<div class="small"> This is a demo text. <<- Small Caps</div>
</body>
</html>
