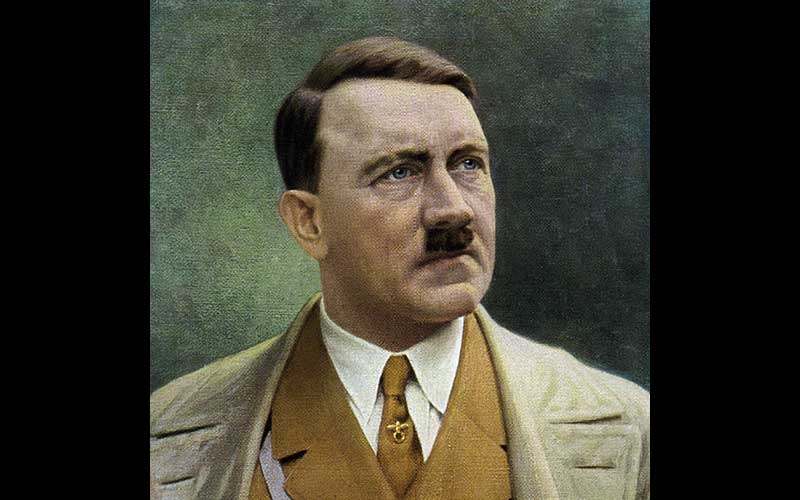
Born on 20 April 1889 in Branau am Inn, a small Austrian town near the Austro-German frontier, Adolf Hitler was the fourth of six children born to Alois Hitler and his third wife, Klara Polzl. Alois wanted his son to follow his example as a civil servant and ignoring his son's desire to attend a classical high school and become an artist, Alois sent Adolf to the ‘Realschule’ in Linz in September 1900. After the sudden death of his father in 1903, Adolf pursued his dream of being an artist and applied for admission to the Academy of Fine Arts in Vienna but was rejected twice.
As his mother died of breast cancer on 21 December 1907, he ran out of money, moved to Vienna, where he was forced to live in shelters for the homeless and earned money by painting and selling scenery and monuments of Vienna. During this period, Adolf became a voracious reader of newspapers and pamphlets containing the thoughts of philosophers like, Houston Stewart Chamberlain, Friedrich Nietzsche, Charles Darwin and developed many of the ideas that would gradually shape Nazi ideology.
In 1913, Hitler moved to Munich and in October 1914, voluntarily joined the Bavarian Army to serve throughout the First Great War. Consequently, he won two decorations for bravery, including the rare Iron Cross First Class, which he wore till the end of his life. During the Battle of the Somme in October 1916, he was wounded in the left thigh by a shell and was temporarily blinded by a British gas attack near Ypres in 1918. A month later, while he was recuperating in a hospital at Pasewalk, northeast of Berlin, he learned about Germany’s defeat in the World War I. Like many Germans, Hitler came to believe that the country suffered the devastating defeat only due to the back stabbing on the home front by the civilian leaders, Marxists, Jews and those who signed the truce that ended the fighting.
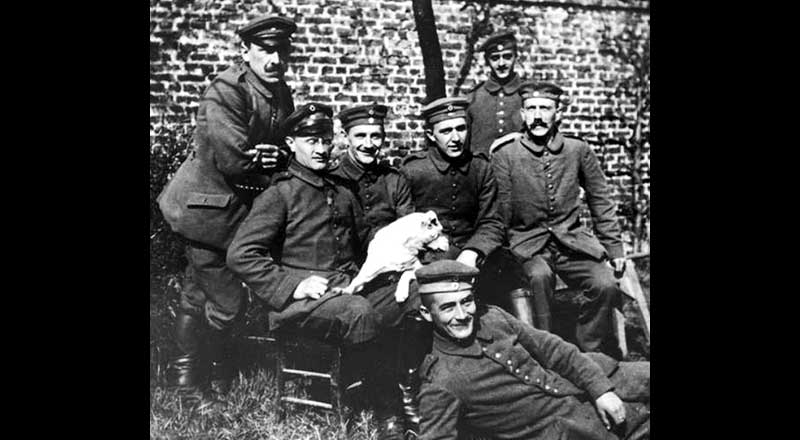

Hitler returned to Munich in late 1918 and in July 1919, he was appointed as the intelligence agent, assigned to influence other soldiers and to infiltrate the German Worker’s Party (DAP). At the DAP, Hitler met Dietrich Eckart, one of the founders of the party, who became Hitler's mentor and introduced him to a wide range of Munich society. To increase its appeal, the DAP changed its name to National Socialist German Workers Party (NSDAP), which is commonly referred to in English as the Nazi Party. Hitler himself designed the party's banner of a Swastika, a hooked cross, in a white circle on a red background. After being discharged from the army on 31 March 1920, he began working full-time for the NSDAP and soon gained notoriety for his rowdy rhetorical speeches against the Treaty of Versailles, rival politicians, and especially against the Jews and the Marxists. Many like-minded former army officers in Munich joined the Nazis, including Ernst Röhm, who recruited the storm division, the Sturmabteilung (SA), which Hitler used to protect party meetings and attack opponents. In English, the members of the unit were known as the Brownshirts.

Hitler wanted to do something spectacular. He wanted to reproduce Benito Mussolini’s ‘March on Rome’ of 1922 by staging his own coup in Bavaria, to be followed by a challenge to the government in Berlin. On the evening of 8 November 1923, Hitler and the SA forced their way into a large beer hall, where Bavaria's de facto ruler, Gustav Ritter von Kahr, was addressing to a crowd of 3000 people. Wielding a revolver, Hitler proclaimed the beginning of a national revolution, but neither the army, nor the state police, joined forces with Hitler. On the following day, Hitler and his followers marched from the beer hall to the Bavarian War Ministry, with the intention to overthrow the Bavarian government. The police, in their turn, promptly dispersed them, while sixteen NSDAP members and four police officers were killed in the failed coup. Hitler was arrested on 11 November 1923 for high treason and was sentenced to five years’ imprisonment in Landsberg Prison. However, though it failed disastrously, the Beer Hall Putsch established Hitler as a national figure and, in the eyes of many, a hero of right-wing nationalism.

Hitler was pardoned by the Bavarian Supreme Court, despite the objections of the state prosecutor and was released on 20 December 1924. While in Landsberg, Hitler started to dictate his book, ‘Mein Kampf’ (My Struggle), the first volume of which was published in 1925. He finished the second volume, while he was relaxing after his release, in the mountain village of Berchtesgaden. Initially, it sold modestly, but with Hitler’s political rise, it became Germany’s best-selling book after the Bible. In his book, Hitler elaborated his nationalistic and anti-Semitic views, which he had begun to develop in Vienna and laid out his plans for the new Germany, as well as the world, that he intends to create. Obsessed with his idea of ethnic purity, Hitler placed the so-called Aryan race at the top of the class. Later, his obsessive pursuit of Aryan supremacy fueled the murder of some 6 million Jews, along with other victims of the Holocaust. According to him, to fulfill the dream, Germany should take over lands to the east, which includes Austria, Czechoslovakia, Poland and Russia, which are occupied by the inferior Slavic peoples. He also opined that, this is not possible by any democratic or parliamentary government, it needs one supreme leader or Führer to fulfill the dream.
By the time of Hitler’s release, the Nazi Party and its affiliated organisations were banned in Bavaria and as the economy had recovered, the support for right-wing causes like Nazism appeared to be waning. On 4 January 1925, in a meeting with the Prime Minister of Bavaria, Hitler promised that he would seek political power only through the democratic process, which consequently paved the way for the lift of the ban on the NSDAP on 16 February. Over the next few years, Hitler created the Schutzstaffel (SS) as a more reliable alternative to the SA, which after 1929, terrorised the rest of occupied Europe during WW II, under the leadership of Heinrich Himmler.
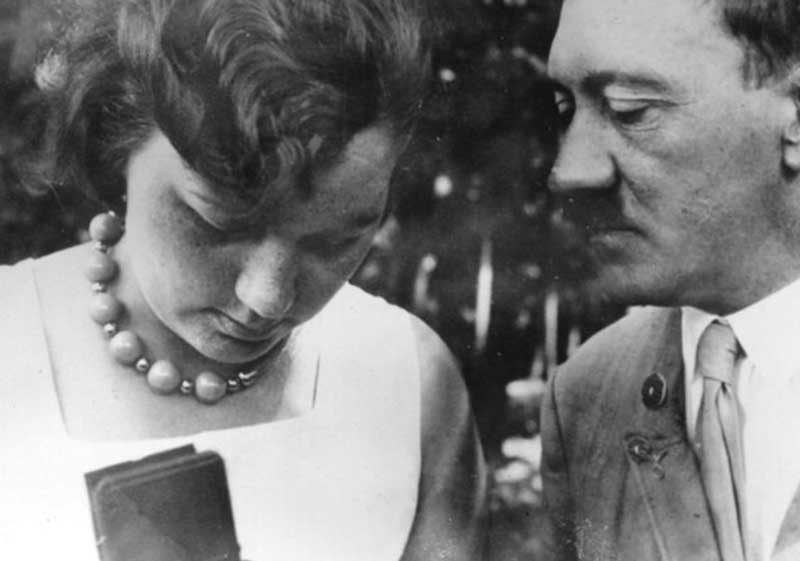

During this period, Hitler spent much of his time at Berchtesgaden, often visited by his half-sister Angela Raubal and her two daughters. However, as he became infatuated with his beautiful blonde niece, Geli, his possessive jealousy apparently led her to commit suicide in 1931. Hitler, devastated by the personal loss, would consider Geli the only true love affair of his life, but soon began a long relationship with Eva Braun, a shop assistant from Munich.

In the 1932 presidential election, Hitler ran against the war hero Paul Von Hindenburg and came in second, garnering more than 35 per cent of the vote in the final election. Although he lost to Hindenburg, the election established Hitler as a strong force to reckon in German politics. After that, since two further parliamentary elections, in July and November 1932, had not resulted in the formation of a majority government, Hindenburg reluctantly named the 43-year-old Hitler as the Chancellor on 30 January 1933, which sparked the stunning rise of the Nazi leader. The day also marked the birth of the Third Reich, or according to the Nazis, the ‘Thousand-Year Reich’.
In fact, Hitler could grab absolute power in Germany largely due to divisions and inaction among the majority who opposed Nazism. As chancellor, Hitler worked against attempts by the NSDAP's opponents to build a majority government and due to the political stalemate, advised Hindenburg to again dissolve the Reichstag, the German parliament. Elections were scheduled for early March, but before that, on 27 February 1933, the Reichstag building was set on fire, allegedly by a Dutch communist. However, later evidences suggested that the fire was actually manufactured by the Nazis, as Hitler badly needed an excuse to step up the political oppression and violence against his opponents.
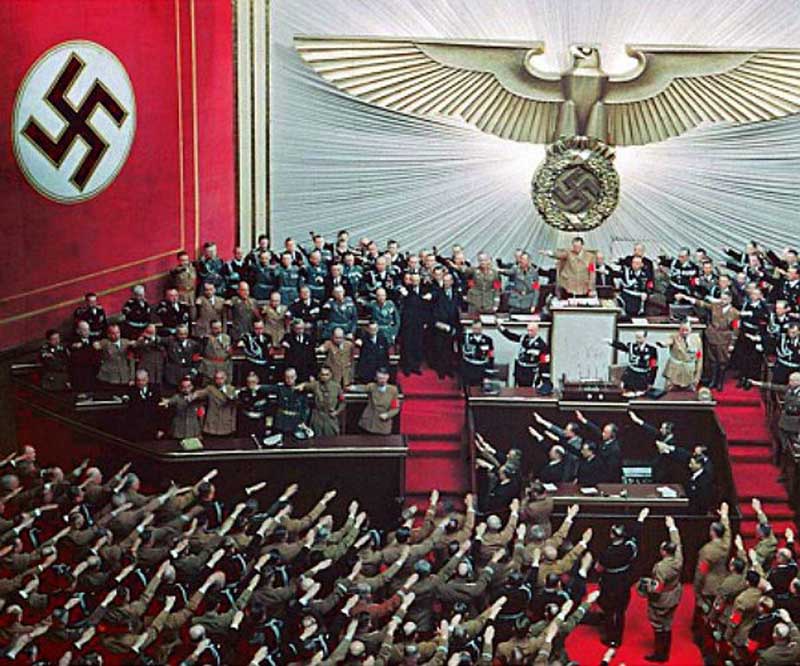

Nevertheless, at the insistence of Hitler, Hindenburg responded with the Reichstag Fire Decree of 28 February, suspending the basic rights of the citizens and allowing detention of anybody without trial. The decree also gave special power to the president to take emergency measures to protect public safety and order. Immediately, activities of KPD (the German Communist Party) were repressed and around 4,000 KPD members were arrested. On 14 July 1933, the Nazi Party (NSDAP) was declared as the only legal political party in Germany and within months all the non-Nazi parties, trade unions and other organizations had ceased to exist. Thus, securing his autocratic power in Germany, Hitler decided to turn his eyes to the rest of Europe.
In October 1933, Hitler withdrew Germany from the League of Nations and purged the entire SA leadership in the Night of the Long Knives, which took place from 30 June to 2 July 1934. Hitler planned and targeted to liquidate Ernst Röhm, along with some other SA leaders and a number of his political adversaries, including former Chancellor Kurt von Schleicher. All of them were surprisingly rounded up, arrested and shot dead. In the same year, after the death of Hindenburg on 2 August, the Military leaders agreed to combine the presidency and chancellorship into one position, meaning Hitler would command all the armed forces of the Reich.
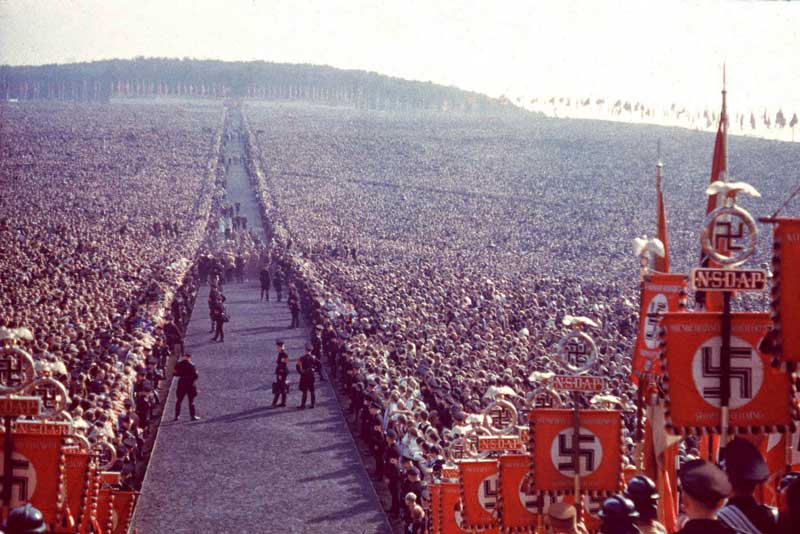

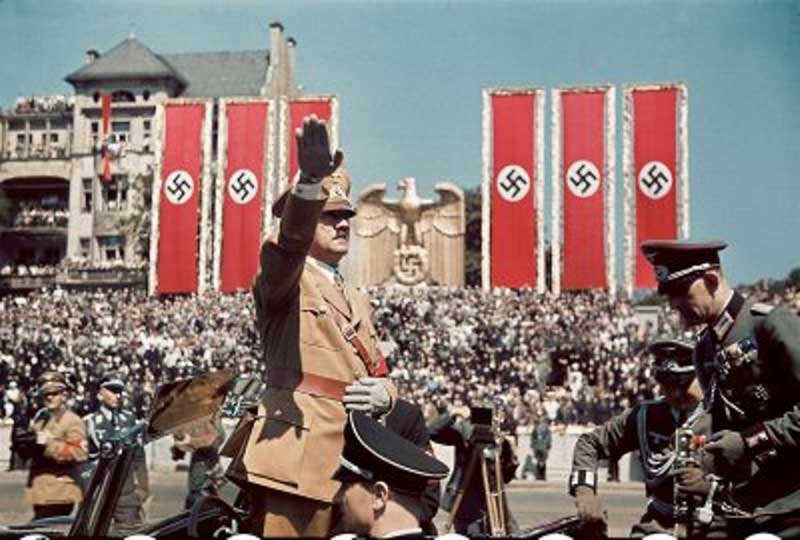
During the month of March 1936, Hitler ordered German troops to reoccupy the demilitarized left bank of the Rhine, against the advice of his generals and over the next two years, concluded alliances with Italy and Japan, annexed Austria and moved against Czechoslovakia, without any objection or resistance from Great Britain, France or any other European country. After the confirmation of the ‘Pact of Steel’ alliance with Italy in May 1939, Hitler signed a non-aggression pact with the Soviet Union and immediately after that, the Nazi troops invaded Poland on the 1st day of September1939, which finally prompted Britain and France to declare war on Germany. The German forces invaded Denmark on 9 April 1940 and on the same day Hitler declared the birth of the Greater Germanic Reich. After that, Germany attacked France through the Ardennes Forest. As the blitzkrieg attack (German word for lightning attack) began on May 10, Holland quickly surrendered, followed by Belgium and Luxembourg.
The Germans made their way to the English Channel, forcing the British and the French forces to evacuate from Dunkirk in late May and France was forced to sign a truce with Germany on June 22.Nevertheless, the British troop continued to fight alongside other British dominions in the Battle of the Atlantic. Hitler had hoped that Britain would propose peace, but when that failed, he ordered a series of aerial attacks on Royal Air Force airbases and radar stations. Apart from that, systematic nightly bombing on London started from 7 September. However, by the end of the month Hitler realized that, only air raid is not sufficient to defeat Britain. He, therefore, ordered to postpone the operation, though the nightly air raids on British cities, including London, intensified and continued for months. On 27 September 1940, Germany, Italy and Japan signed the Tripartite Pact, which came known as the Axis alliance and on 22 June 1941, contravening the Hitler-Stalin Non-Aggression Pact of 1939, over 3 million Axis troops attacked the Soviet Union.

Hitler intended to destroy the Soviet Union and seize its natural resources for his subsequent aggression against the Western European powers. Within two months of the assault, the Axis troops had advanced 500 km (310 mi) and won the Battle of Smolensk, fought around the city of Smolensk between 10 July and 10 September 1941. However, at that stage, when his army is within 400 km of Moscow, Hitler ordered to stop advancing to the Soviet capital and diverted his troop to aid the encirclement of Leningrad and Kiev. The decision provided an excellent opportunity for the Red Army to mobilise fresh reserves and is considered by many as one of the major factors that caused the failure of the Moscow offensive. When the postponed attack resumed in October 1941, it ended disastrously during the harsh wintry days of December of the same year.
On the other front, four days after Japan attacked the American fleet at Pearl Harbour on 7 December 1941, Hitler declared war against the United States. However, German forces were defeated in the Second Battle of El Alamein in late 1942, smashing Hitler’s intention to seize the Suez Canal. In the Russian front, as Hitler repeatedly refused to withdraw the army, more than 200,000 Axis soldiers were perished and 235,000 were taken to prison at the Battle of Stalingrad. Thereafter, the Germans were also decisively defeated at the Battle of Kursk. With the passing of time, Hitler’s military judgements became increasingly erratic and Germany's military and economic position deteriorated, as did Hitler's health. He became increasingly unwell, isolated and fully dependent on medications.
The Soviet Union steadily forced Hitler's armies to retreat along the Eastern Front throughout 1943 and 1944. However, after a few months of the successful Allied invasion of Normandy on June 1944, when the Allies started liberating cities across Europe, many German officers knew it for sure that defeat was inevitable and only a matter of time and under such circumstances, continuing under Hitler's leadership would lead to complete destruction. In fact, several attempts were made on his life, including one that came very close to succeeding in July 1944, when a bomb planted by Col. Claus von Stauffenberg exploded during a conference at Hitler’s headquarters in East Prussia.
After a military conference on 22 April, Hitler asked everyone to leave the room, except Wilhelm Keitel, Alfred Jodi, Wilhelm Burgdorf and Hans Krebs. Then, he launched into a tirade against the treachery and incompetence of his commanders and declared for the first time that, everything was lost. The Red Army had surrounded Berlin by 23 April and at midnight on the night of April 28-29 Hitler married Eva Braun in his Berlin bunker.
On 30 April 1945, when the Soviet troops were within a block or two of the Reich Chancellery, Hitler shot himself in the head, while Braun bit into a cyanide capsule. Their bodies were carried out to the garden, located behind the Reich Chancellery and placed in a bomb crater. After that, the bodies, doused with petrol were set on fire.
